Click to Skip Ahead
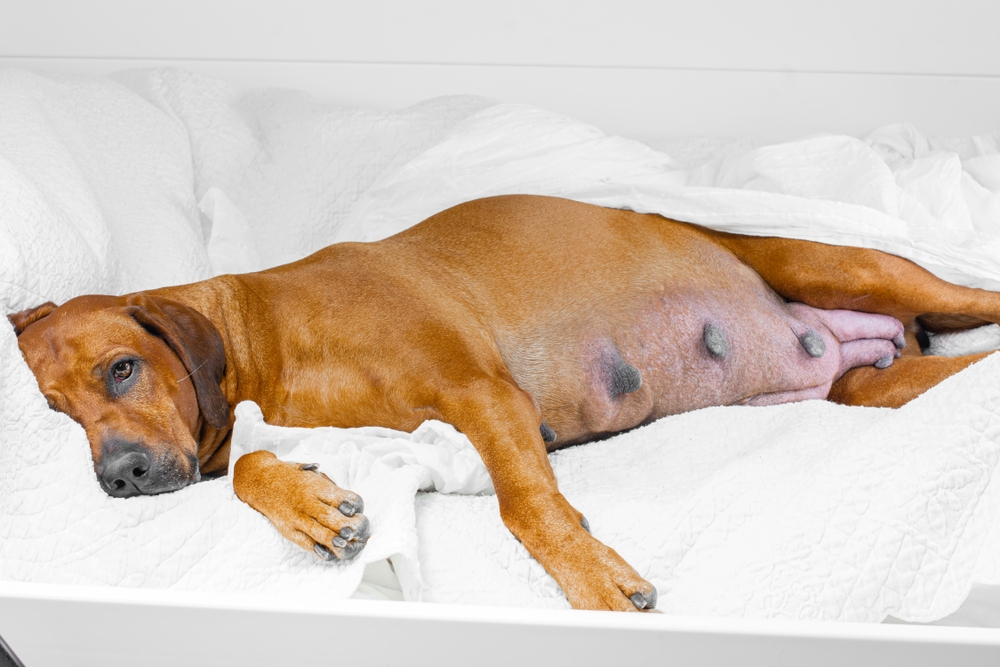
Puppies have so much growing up to do! Part of that process involves developing a healthy and strong immune system. As puppies age, they start to lose the protective antibodies that they acquired from their mother and begin to develop their own immune defenses.
However, this transition can make them vulnerable to sickness, especially those that are not fully vaccinated. The following list highlights the common illnesses and diseases that puppies can acquire.
The 8 Common Puppy Illnesses & Diseases to Be Aware Of
1. Parvovirus (Parvo)
Parvovirus attacks the gastrointestinal system and causes signs like vomiting, bloody diarrhea, lethargy, anorexia, and dehydration. The virus is transmitted through contaminated feces, is highly contagious, and can prove fatal. The virus is also hardy in the environment and may survive for months or years. Ideally, puppies diagnosed with parvo should be hospitalized, as there is no cure for the disease, only supportive care.

2. Distemper
Like parvo, distemper is a highly contagious and often fatal virus. It can attack the nervous, gastrointestinal, and respiratory systems, producing signs like seizures, head tilt, circling, fever, lethargy, coughing, and discharge from the eyes and nose. Some puppies develop thickened paw pads and may have dental abnormalities if they survive the disease. Other puppies may have neurological abnormalities that persist for life. Distemper virus can be transmitted in respiratory droplets from sneezing or coughing or from contaminated food and water bowls. There’s no cure but there is supportive care.
3. Canine Infectious Respiratory Disease (Kennel Cough)
Canine infectious respiratory disease is a common and easily transmissible respiratory virus among dogs. It may be caused by bacteria (like Bordetella bronchiseptica), a virus (like canine parainfluenza virus or canine coronavirus), or both. Most infections resolve on their own in 1–3 weeks, while more severe signs may require treatment like antibiotics, an anti-inflammatory, and a cough suppressant from your veterinarian. Severe cases of kennel cough may lead to pneumonia.
If your puppy is diagnosed with kennel cough, use a body harness instead of a collar so the pressure does not irritate their trachea.

4. Leptospirosis
Leptospirosis is an infection caused by bacteria (Leptospira) that are shed through infected urine. It can be transmitted in contaminated water sources that are visited by wildlife and livestock, soil, bedding, or any surface containing infected urine. The infection attacks the kidneys and liver and is typically treated with antibiotics and aggressive fluid therapy in more severe cases.
Despite treatment, the disease can be fatal. It is also contagious to humans, making it a zoonotic disease. Care must be taken around puppies and dogs diagnosed with leptospirosis to avoid catching it. This includes wearing disposable gloves and washing your hands after cleaning up after your dog.
5. Adenovirus
Adenovirus is a virus that causes infectious canine hepatitis in puppies and dogs. It usually attacks the liver and is spread through contact with an infected animal or surface. Signs may include lethargy, inappetence, fever, vomiting, and diarrhea. There is no cure, only supportive care. Unfortunately, the survival rate is low, only 1–30%.

6. Rabies
Rabies is always fatal once clinical signs develop. This deadly virus is shed in saliva and transmitted through the bite of an infected animal. The signs may include behavioral changes, neurological abnormalities, hyperexcitability, or paralysis. Rabies is also contagious for humans, so if you’ve been bitten or scratched by a strange dog, you must seek medical care immediately.
7. Parasites
Internal and external parasites can affect puppies. Common internal parasites include roundworms, hookworms, stomach worms, tapeworms, giardia, coccidia, and heartworms. External parasites include fleas, ticks, mites, and lice.

8. Vomiting and Diarrhea
Vomiting and diarrhea in a puppy can be caused by several underlying conditions that a veterinarian should evaluate. Common conditions include foreign bodies, toxins, stress, sudden diet changes, or bacterial, viral, or parasitic-related illnesses.
How Can I Keep My Puppy Safe?
Start with the core vaccinations, such as DA2PPv, when your puppy reaches 6–8 weeks old.
- Distemper virus
- Adenovirus type 2
- This cross-protects against Adenovirus type 1, which causes infectious canine hepatitis; type 2 causes tracheobronchitis.
- Parainfluenza (tracheobronchitis)
- Parvovirus
To provide the best protection, it’s administered every 2–4 weeks until your puppy is 16–20 weeks old.
Another vaccine to consider is the one for canine infectious respiratory disease, especially the one caused by the bacterium Bordetella bronchiseptica. Puppies can get this starting at 8 weeks of age, especially if they’re exposed to other dogs. It’s also known as kennel cough or infectious tracheobronchitis and is common in dogs in kennels or boarding situations.
The leptospirosis vaccine can be started at 12 weeks of age. At this time, puppies can also be dewormed and started on flea-and-tick prevention to prevent infestations. Depending on the age of your puppy and your state laws, puppies can receive a rabies vaccine starting at 12–16 weeks of age. This would be best discussed with your veterinarian.
Ideally, your puppy should be fully vaccinated before interacting with other dogs at around 16 weeks of age. However, socialization in puppies is also crucial. If there are puppy socialization classes near you, you may be able to sign up for one that has puppies of similar ages and vaccine status. If you would like to bring your puppy out in public, you can do so by holding and carrying them around, to lessen the chance of disease transmission from other dogs.

Conclusion
Puppies have an underdeveloped immune system, which can make them more susceptible to certain diseases. Taking precautions like vaccinating and supervising interactions with other dogs and places is crucial. Avoid places where the unknown vaccination status of dogs is frequent, such as dog parks, until your puppy is fully vaccinated.
Featured Image Credit: Hryshchyshen Serhii, Shutterstock