Click to Skip Ahead
Dental disease is one of the most widespread and often underestimated conditions that significantly impact the health of dogs worldwide. One of the main problems is that our dogs will often suffer in silence, and it’s not always obvious to us as owners just how severe the problem is. Making things even more difficult is that one of the signs of a major dental problem may not immediately look like a tooth problem at all.
There are a number of ways in which a tooth abscess can appear, with some of the more common locations and presentations being a swelling below the eye or a chronically snotty nose, so you can see why some owners may not recognize this as being an issue with the mouth. Let’s take a closer look at how and why tooth root abscesses form, how to recognize the signs, and what you can do to prevent them.
What Is a Tooth Root Abscess?
If you’ve ever experienced the pain of an infected tooth, you might think it would be impossible for your dog to carry on life as normal with one, but surprisingly, most dogs will find ways to cope with the pain and lead you to believe that there is no problem. You would be amazed at the state of some of the teeth we see in veterinary practice—mouths so full of calculus, inflammation, and disease that it’s a wonder these dogs can eat at all! And yet, most of the time, they do, placing their bodies and immune systems under considerable strain.
When a tooth becomes infected, the nerves and blood supply become inflamed and painful, as bacteria and pus start to invade the tissue surrounding the root. In some cases, this weakens the connective tissue that holds the tooth in place—called the periodontal ligament—causing the tooth to become loose. In other cases, the infection pushes deeper into nearby tissue, resulting in the formation of an abscess.
With very little room to expand, these abscesses can invade the jaw, leading to a condition called osteomyelitis (infection of the bone), or they may push their way toward the skin. This is often the case when abscesses form from the roots of the large teeth, where the roots are much closer to the surface.
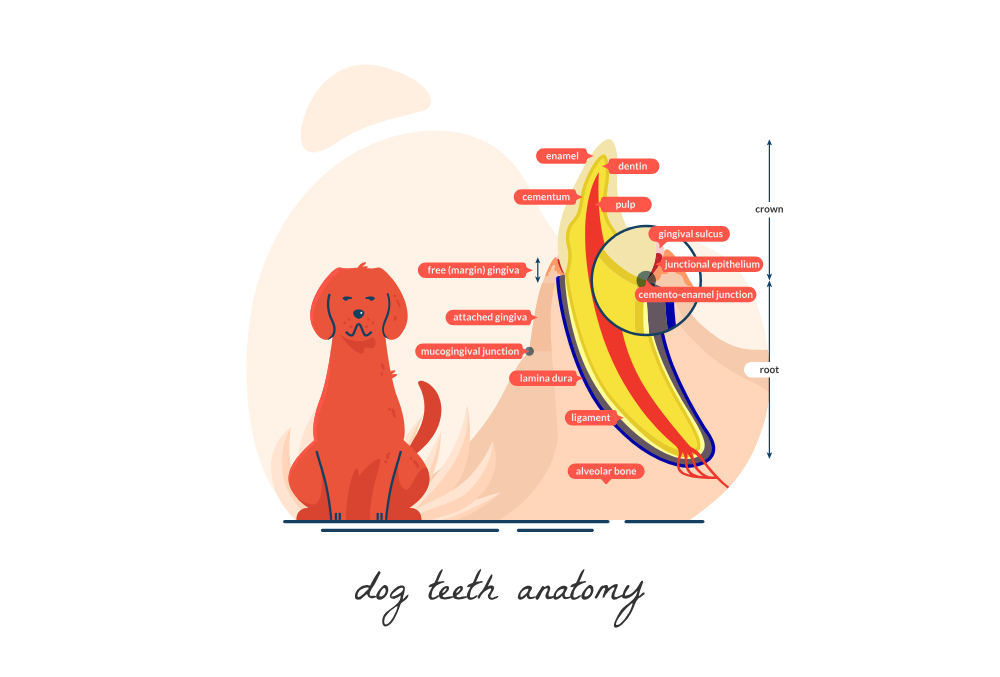
Some Basic Anatomy
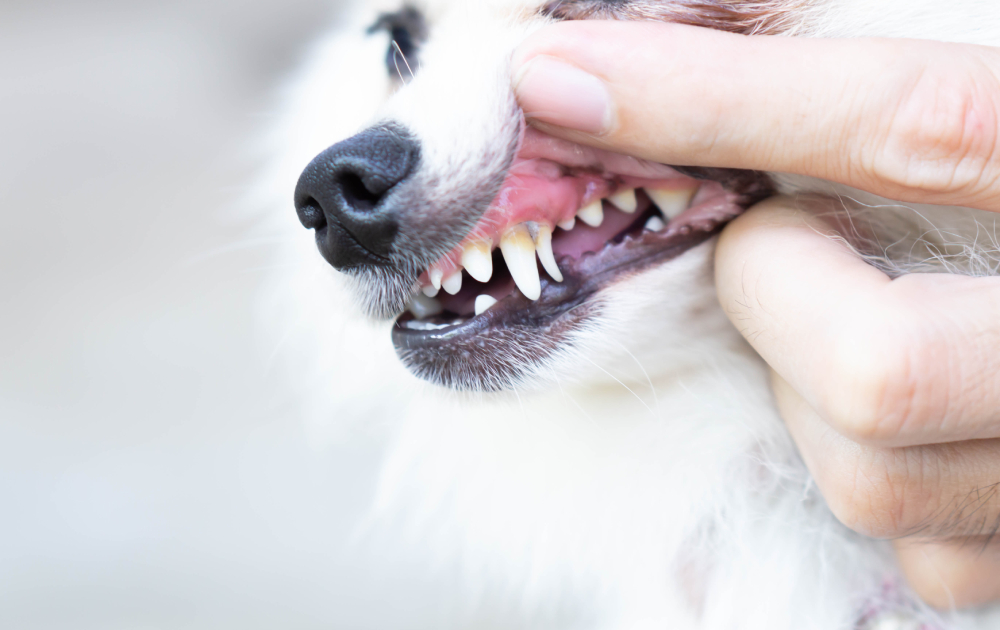
Although infection and abscess can affect any tooth, the ones most likely to show external signs are those with the largest roots: the upper canine tooth and the upper fourth premolar, also known as the carnassial tooth.
The close proximity of the root of the upper canine to the nasal passages means that when this tooth becomes infected, nasal discharge is one of the most common clinical signs. In the case of the upper carnassial, the abscess pushes through a thin area of bone just in front of the zygomatic arch (cheekbone), resulting in swelling below the eye.
Ironically, the point at which the infection looks worse to us often feels better to the dog, as the pressure that has been building up is somewhat relieved. Antibiotic treatment will often alleviate the swelling and discharge for a time but rarely offers long-term resolution.
What Causes a Tooth Root Abscess?
The most common reasons for a tooth root abscess (TRA) to form are chronic dental disease and tooth trauma. Tartar and calculus accumulate on the tooth surface, weakening the protective enamel and dentin layers, while inflammation of the gums (gingivitis) weakens the stability of the tooth. If bacteria penetrate the inner layer of the tooth (the pulp), the infection will kill off the nerves and blood supply to the tooth, and penetrate the surrounding area.
Tooth abscesses can also occur as the result of physical damage to the tooth, such as a fracture or chip that exposes the pulp. This can also happen with gradual wearing of the teeth, particularly in dogs that chew stones or tennis balls.
What Are the Signs of Tooth Abscesses in Dogs?
The signs that a dog is suffering from a TRA will often depend on which, and how many, teeth are affected, but can include:
- Nasal discharge/sneezing (usually one side but can be bilateral, may contain pus or blood)
- Swelling, redness, tenderness, or hairless patch under the eye (with or without blood and/or pus)
- Bad breath
- Unusual amount of drooling, particularly from one side/area of the mouth (with or without blood and/or pus)
- Dropping food out the mouth
- Favoring one side of the mouth when eating
- Pain around the head, face, and muzzle (may become “head shy”)
- Weight loss
- Reduced appetite
- Dull, depressed demeanor, loss of interest in normal activities
Sometimes the signs of a TRA are quite obvious, but often your dog will mask the pain and give very little indication of there being a problem, making regular examinations with your vet an essential part of your dog’s healthcare.

How Are Tooth Abscesses Diagnosed?
Initially, your vet will make a provisional diagnosis of a TRA based on your dog’s clinical signs and examination. The next step of the diagnosis will be to admit your dog for a general anesthetic to perform a dental examination and dental X-rays to confirm the presence of an abscess, assess the extent of damage, check the other teeth, and formulate the best plan of action.
How Are Tooth Abscesses Treated?
The first step of treating a TRA is pain relief and antibiotics. In the case of chronic dental disease or fracture, the affected tooth needs to be extracted, as the pulp and surrounding tissue are usually too damaged to be salvaged. When a TRA has occurred as the result of minor trauma, a root canal can be attempted to preserve the tooth, but if there is significant damage to the periodontal ligament or dentin, this is unlikely to be successful.
Fortunately, dogs do very well following tooth extractions and aren’t quite as concerned about the aesthetics as we are!

Can Tooth Abscesses Be Prevented?
There are several steps you can take to hugely reduce your dog’s risk of developing a tooth root infection and abscess, including:
- Maintaining good dental hygiene with regular brushing
- Providing appropriate foods and VOHC approved dental chews
- Stopping your dog from chewing stones, sticks, or hard toys
- Ensuring your dog has a thorough dental examination as part of their annual health check with the vet
Can My Dog’s Tooth Abscess Be Treated Without Dental Surgery?
In rare cases, where an abscess has formed as the result of a minor trauma, such as a stick injury, a course of antibiotics may resolve the infection completely. Most of the time, however, antibiotics will provide temporary relief by treating the infection, but abscesses will continue to form until the underlying problem has been addressed.
Final Thoughts
Tooth abscesses affect dogs more often than you might think; probably more often than are diagnosed. The signs of a tooth infection are not always immediately obvious, and our dogs are masters of pushing on through the pain, which is why we need to be extra vigilant.
Some of the best ways to try to prevent tooth abscesses in dogs are to get into the habit of keeping your dog’s teeth clean and healthy from a young age, keep sharp and hard objects out of their mouths, and make sure your vet performs a thorough dental exam at least once a year. If you spot any changes in the way your dog is chewing their food or if they have a chronically runny nose or a swelling or lesion under their eye, you might be seeing the signs of a tooth root abscess, so don’t hesitate to make an appointment with your vet.
Featured Image Credit: MRAORAOR, Shutterstock